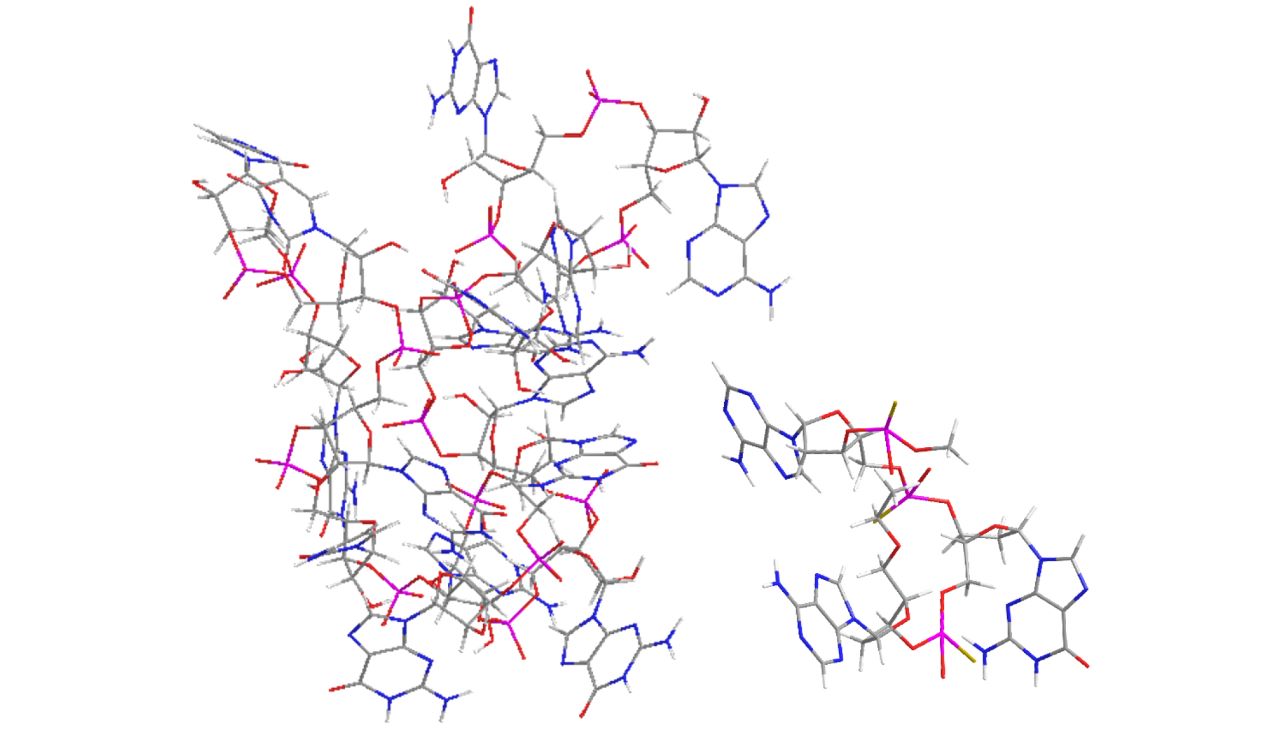
Overproduction of proteins can lead to the development of many human diseases.
Oligonucleotide-based therapeutics, drugs designed on the basis of DNA/RNA sequence information, specifically and dramatically decrease the level of disease-associated proteins, including targets once considered un-druggable.
Complementary to the RNA encoding for a given protein, oligonucleotide therapeutics such as antisense oligonucleotides (ASO), upon binding, can elicit RNA degradation with consequent inhibition of the target protein expression.